Client SDK States & Lifecycle
Nimbus SDK Experiment States and Lifecycle
Authors: Ryan Kelly
Reviewers: Kate Hudson, Tim Smith
Status: Draft as of November 2020; see the changelog for updates
Introduction
This document provides a high-level overview of the lifecycle of a Nimbus experiment, from the point of view of the client SDK. It's in part an adjunct to the Nimbus Experiment Publishing Lifecycle.
The behaviour of API calls to the Client SDK will depend on both the last observed server-side experiment state, and the current local client state, and the SDK will emit telemetry based on the local state of each experiment.
I happen to think that these states could map nicely to some Rust Enums, but your mileage may vary.
Key Concepts
Treatment
We'll use "treatment" to refer to the change in client behaviour that's triggered by an experiment. This might be a small change in colour or wording, or may provide some much larger piece of new UX. The details and scope don't matter for our purposes here, what matters is having a word that means "the user is experiencing the effects of the experiment".
Enrollment
Enrollment is the process of the client SDK deciding whether this client should be part of the experiment and if so, what branch it should be assigned to. We'll emit an enrollment telemetry event when this happens.
Once a client is enrolled in an experiment, it will tag its telemetry pings with that experiment and branch information so that they can be identified for analysis.
Enrolled clients will remain enrolled and assigned to the same branch until the experiment ends, or until they reset their experiment state by disabling telemetry. A client may disable the treatment under various circumstances, but it's important that it continue reporting that it was enrolled in the experiment, to help with data analysis.
Note that it's possible for an experiment to be closed for new enrollments, while continuing to be active for and showing its treatment to previously-enrolled clients.
Exposure
Exposure is the process of actually showing the treatment. In other words, it's when we change client behaviour based on the experiment branch in which the client was enrolled, or when we would have changed behaviour if the user was not in the control group. We'll emit an exposure telemetry event the first time this happens.
Note that it's possible for a client to be enrolled in an experiment but never be exposed to its treatment, for example if the user never uses the part of the client app that is affected by the treatment.
Disqualification
After a client is enrolled in an experiment, we may need to disable that experiment's treatment for various reasons, such as:
- The user explicitly opts out of the experiment, or of all experiments.
- The application code detects that it cannot show the treatment.
- The targeting parameters change in a way that excludes the client.
We'll emit a telemetry event when this happens.
Importantly, if the client was already enrolled in an experiment, then it will continue to tag its telemetry pings with the enrolled experiment and branch information, even if it has become disqualified.
Server-Side Experiment States
The Nimbus experiment publishing workflow moves each experiment through several different states, reflected in the experiment data published to the Remote Settings server. Transitions between the states are triggered by updates published to Remote Settings. (TODO: maybe also by the passage of time as observed by the RS server?)
Note that we are only interested in states that are observable by the client; the experiment publishing workflow has additional states for internal use that are not represented here.
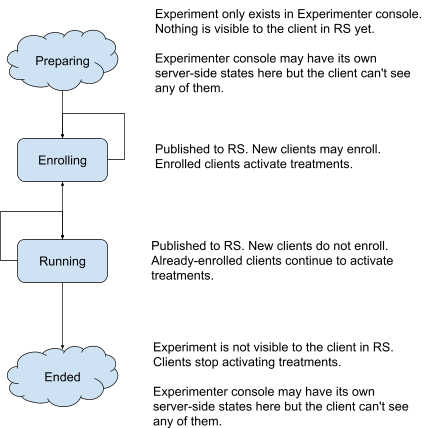
The "Preparing" State
Before an experiment becomes visible to clients in Remote Settings, it may go through a series of drafts and adjustments and approvals in the Experimenter console. This is represented in the server-side workflow by several different states, but since it is completely invisible to the Client SDK these will not be discussed further in this document.
Transitions:
- To Enrolling state, by being made visible to clients in Remote Settings.
The "Enrolling" State
This is the first phase of an experiment going "live" and starting to show up in the user experience. It's indicated by the experiment being visible to clients in Remote Settings with isEnrollmentPaused set to false.
Clients that observe an experiment transition to this state should check whether to enroll in the experiment (N.B. this includes a self-transition from Enrolling -> Enrolling that is accompanied by a change in the published experiment config, which might change enrollment decisions).
While the experiment is in this state, enrolled clients should activate the experiment treatment appropriate for their enrolled branch, and report telemetry about it.
Transitions:
- To Running state, when a Remote Settings update changes isEnrollmentPaused to true.
- To Enrolling state, when a Remote Settings update changes other experiment parameters.
- To Ended state, if the experiment ceases to be visible in Remote Settings.
The "Running" State
This is the second phase of an experiment being live and showing up in the user experience. It's indicated by the experiment being visible to clients in Remote Settings with isEnrollmentPaused set to true.
While the experiment is in this state, clients that are not already enrolled in the experiment should not enroll themselves, even if the experiment config changes in a way that would otherwise cause them to enroll. Already-enrolled clients should continue to activate the experiment treatment appropriate for their enrolled branch, and report telemetry about it.
Transitions:
- To Enrolling state, when a Remote Settings update changes isEnrollmentPaused to false.
- To Running state, when a Remote Settings update changes other experiment parameters.
- To Ended state, if the experiment ceases to be visible in Remote Settings.
The "Ended" State
An experiment ends when it ceases to be visible to clients in Remote Settings. As with the "Preparing" state, there may be multiple server-side states involved in ending an experiment, but since they are completely invisible to the Client SDK these will not be discussed further in this document.
Transitions:
- None, this state is terminal.
Errors:
- TODO: should we log some sort of error if we observe an experiment coming back to life after it was ended?
Client-Side Experiment States
Each Nimbus client will also have its own local state for each experiment, based on the observed history of the server-side experiment states that it has read from the Remote Settings server. Transitions between the states are triggered by observing experiment config changes when querying the Remote Settings server, and by the passage of time on the client.
The "Unknown" State
Before an experiment is published to Remote Settings, obviously the client SDK can't know anything about it. But there may be client code that calls the SDK asking whether to activate treatments for this as-yet-unknown experiment, so it's worth representing this state explicitly.
Transitions:
- To Enrolled state, by observing the experiment in Remote Settings for the first time, the experiment being in Enrolling state, and bucketing logic dictating that the client should enroll in a branch of the experiment.
- To NotEnrolled state, by observing the experiment in Remote Settings for the first time, but deciding not to enroll based on the observed experiment state or local config.
The "NotEnrolled" State
In this state, the client has observed the existence of an experiment in Remote Settings and has stored a local copy of the current experiment config, but based on that config has decided not to enroll in the experiment.
Transitions:
- To Enrolled state, when the experiment transitions to Enrolling state, and bucketing logic dictates that the client should enroll in a branch of the experiment.
- (N.B. this includes the experiment transitioning Enrolling -> Enrolling with an update to the experiment config)
- (N.B. the bucketing logic may depend on the state of other experiments, in the case of conflicts between multiple experiments)
- To Errored state, encountering some unrecoverable error in the experiment config.
- To Discarded state, when the experiment transitions to Cancelled or Completed.
The "Enrolled" State
In this state, the client has previously observed the experiment in Enrolling state and has been bucketed into a branch of the experiment. It persists the selected branch so that it can consistently reference it even if the experiment config changes in future.
Transitions:
- To Disqualified state:
- When the user explicitly opts out of participating in this experiment.
- When the user explicitly opts out of participating in experiments in general.
- When application code makes an explicit API call to disable this experiment.
- When the experiment transitions to Enrolling or Running state, and its targeting expression no longer matches the client.
- (N.B. this includes the experiment transitioning Enrolling -> Enrolling with an update to the experiment config, which can re-trigger bucketing evaluation)
- When encountering some unrecoverable error in the experiment config.
- To WasEnrolled state:
- When the experiment transitions to Cancelled or Completed
- (i.e. When a valid response is received from Remote Settings and the experiment is no longer present in the Remote Settings collection).
- When the experiment transitions to Cancelled or Completed
- To Discarded state, when the user entirely disables telemetry in their client.
The "Disqualified" State
In this state, the client had previously enrolled in the experiment, but some change has occurred that means we can no longer show them to experiment treatment. The client will continue to tag its telemetry pings with enrollment data, but will not activate the treatment.
Transitions:
- To WasEnrolled state:
- When the experiment transitions to Cancelled or Completed
- (i.e. When a valid response is received from Remote Settings and the experiment is no longer present in the Remote Settings collection).
- When the experiment transitions to Cancelled or Completed
- To Discarded state, when the user entirely disables telemetry in their client.
Note that once a client has been disqualified from an experiment, it is not possible for it to be resume showing the experiment treatment.
The "WasEnrolled" State
In this state, the client remembers that it was previously enrolled in an experiment and may report diagnostic telemetry about this fact, but the experiment has ended and its treatments are no longer activated.
WasEnrolled experiments are shown in about:studies:
It's also useful for analysis to have a period of observation (say 30 days?) after an experiment ends in which we still tag telemetry pings with the experiment branch info.
Transitions:
- To Discarded state after 31 days have passed since it entered the WasEnrolled state, according to the client's local clock.
The "Errored" State
A special state into which the client transitions if it observed any unexpected behaviour, such as invalid experiment config or unexpected experiment-state transitions. In this state the client may log diagnostic telemetry but will not enroll in the experiment nor activate any experiment treatments.
It is not possible to escape this state, except by discarding the experiment information.
Transitions:
- To Discarded state, when the experiment transitions to Cancelled or Completed.
The "Discarded" State
This isn't really a state, it's just to mark on the diagram the point at which we discard historical data about the experiment from the client's local storage.
Once the client reaches this state, it stops tagging its telemetry pings with information about the experiment.
Telemetry
Nimbus clients will submit telemetry via Glean. The full set of experiment-related telemetry is defined in the Nimbus Engineering Confluence page.
Nimbus will use the Glean Experiments API to tag outgoing metrics pings with information about enrolled experiments:
- After initialization, the Nimbus SDK will list all known experiments in Enrolled, Disqualified or WasEnrolled state and call
setExperimentActive(slug, branch)to tag outgoing telemetry pings with the enrolled branch of that experiment. - When an experiment transitions to Enrolled state, the Nimbus SDK will call
setExperimentActive(slug, branch)to tag outgoing telemetry pings with the enrolled branch of the new experiment. - When an experiment transitions from WasEnrolled to Discarded, the
Nimbus SDK will call
setExperimentInactive(slug)to cease tagging outgoing telemetry pings with information about the experiment. Note, that Glean does not cache or persist the experiment API info, so it's important to callsetExperimentActiveon every run, preferably close to startup so that it can annotate any custom pings that may be sent out early during app launch. ThesetExperimentInactiveonly needs to be called if we have calledsetExperimentActivefor that experiment in the same app run.
Nimbus will also emit Glean events on key experiment state transitions:
- An "enrollment" event, when an experiment enters the Enrolled state.
- Event field "experiment" records the experiment slug.
- Event field "branch" records the branch into which the client enrolled.
- Event field "enrollmentId" contains a randomly-generated identifier for this enrollment.
- A "disqualification" event, when an experiment enters the Disqualified state.
- Event field "experiment" records the experiment slug.
- Event field "branch" records the branch into which the client enrolled.
- Event field "enrollmentId" contains the enrollment id from the corresponding "enrollment" event.
- Event field "reason" containing the reason for disqualification, as one of the following values:
- "optout"
- "targeting"
- An "unenrollment" event, when an experiment enters the WasEnrolled state.
- Event field "experiment" records the experiment slug.
- Event field "branch" records the branch into which the client enrolled.
- Event field "enrollmentId" contains the enrollment id from the corresponding "enrollment" event.
Nimbus will also emit Glean events when the client code calls experiment-related APIs:
- An "exposure" event, when client code calls
activateExperimentorisFeatureEnabledfor the first time, and the experiment is in Enrolled state.- Event field "experiment" records the experiment slug.
- Event field "branch" records the branch into which the client enrolled.
- Event field "enrollmentId" contains a randomly-generated identifier for this enrollment.
Client Behaviours
When asked if an experiment is active
- Get the current client state and last-seen server state for the named experiment.
- If the client state is Enrolled, return true.
- Otherwise, return false.
When asked for the current branch of an experiment
- Get the current client state and last-seen server state for the named experiment.
- If the client state is Enrolled, return the enrolled branch and its config.
- Otherwise, return None.
When asked for the current config of a feature
- Get the current client state and last-seen server state for all experiments.
- Discard any experiments whose client state is not Enrolled.
- For each remaining experiment:
- Get the branch config for the Enrolled branch.
- If it does not contain config for the named feature, discard the experiment
- If more than one experiment remains, TODO this is an error right? report it somehow.
- If exactly one experiment remains, return the feature config from its Enrolled branch.
- Otherwise, return None.
When a server update transitions an experiment to "Enrolling"
- If the current client state for the experiment is Unknown or NotEnrolled:
- Get the current state for all known experiments that conflict with this one.
- Evaluate targeting/bucketing/etc, if it says to enroll, set client state to Enrolled.
- TODO: trigger a notification in the client app somehow, to redraw UI etc?
- Otherwise, set client state to NotEnrolled.
- If the current client state for the experiment is Enrolled:
- TODO: what exactly? How does an existing enrollment change in response to updated experiment config?
- Otherwise, set the current client state for the experiment to Errored and log some diagnostic telemetry.
When a server update transitions an experiment to "Paused" or "Running"
- If the current client state for the experiment is Enrolled:
- TODO: trigger a notification in the client app somehow, to redraw UI etc?
When a server update transitions an experiment to "Cancelled" or "Completed"
- If the current client state for the experiment is Enrolled:
- TODO: trigger a notification in the client app somehow, to redraw UI etc?
- Set client state to WasEnrolled.
- Otherwise, discard the experiment state.
During some periodic cleanup process
- For each experiment in the WasEnrolled state:
- If it has been more than N days since we entered that state, discard the experiment state.
References
- Nimbus - Experiment Publishing Lifecycle and Permissions
- Unpacking Unenrollments, an explainer for data analysis needs around unenrolling/disabling experiments
Changelog
2021-04-13 (dmose):
- Moved from Google Doc, converted to MDX format, and commited to DocsHub.
2020-11-18 (rfkelly):
- Renamed "activation" to "exposure" in line with terminology discussion from Nimbus Architecture Group meeting.
2020-11-13 (rfkelly):
- Renamed "disabled" state to "disqualified"
2020-11-11 (rfkelly):
- Added the "disabled" state to client states.
- Added the "telemetry" section.
2020-10-30 (rfkelly):
- Added the key concept of "disablement" as distinct from unenrollment.
- Simplified server states by:
- combining "drafting + pending" into "preparing".
- also removed hypothetical logic around handling of "startDate" in order to start a pending experiment; it starts when visible in Remote Settings.
- combining "completed + cancelled" into "ended".
- removed "paused" since it doesn't sound like we have such a state that's distinct from "running".
- combining "drafting + pending" into "preparing".