Jetstream Architecture and Operations
Jetstream is part of the Cirrus ecosystem and depends on some external services.
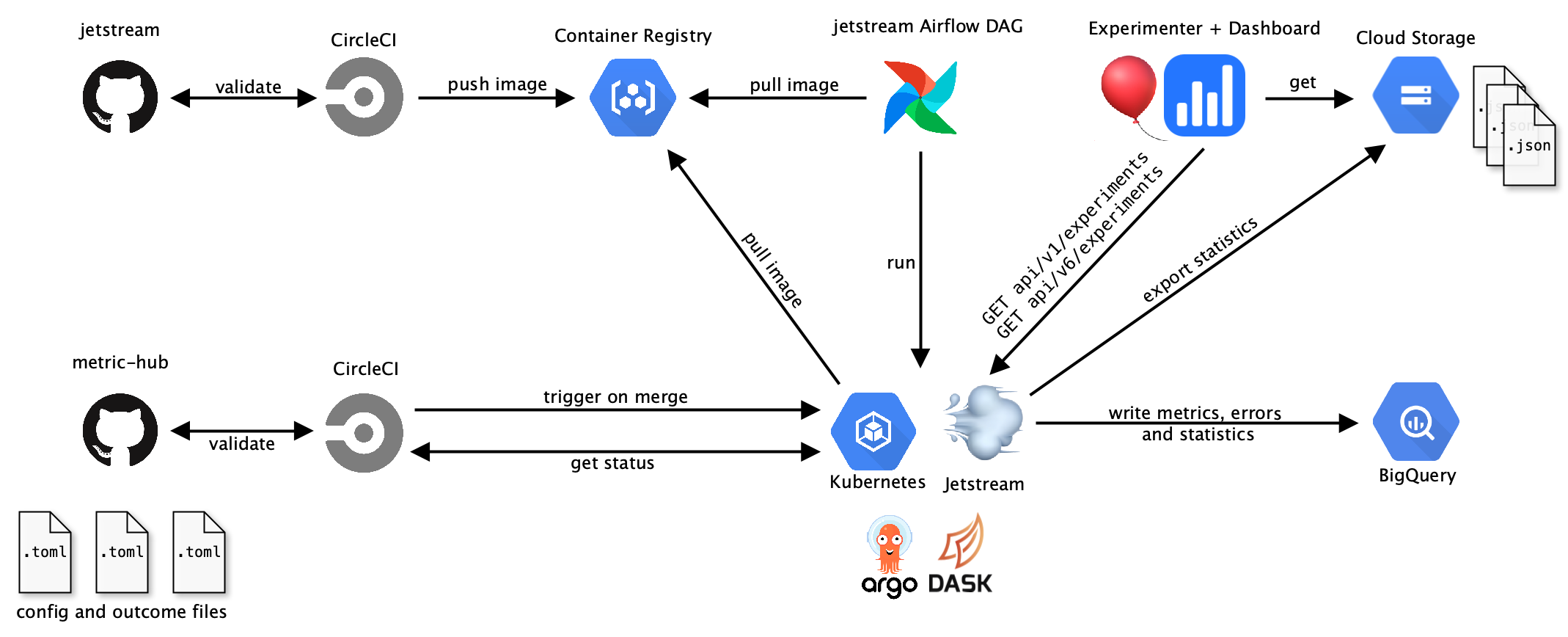 High-level overview of Cirrus
High-level overview of Cirrus
Jetstream is scheduled to run in Airflow daily. The daily runs will analyze all experiments that are currently active or just ended the day before and write metrics, statistics and errors for each experiment to BigQuery. Active V1 experiments and V6 experiments (Nimbus experiments) are retrieved from the Experimenter API.
Jetstream also fetches custom experiment and outcome configs from the jetstream/ directory in metric-hub for analysis. When a new custom config gets merged into metric-hub, the CI will trigger Jetstream to re-run all analyses for the experiment affected by the config. CircleCI will report on the status of the analysis run and link to the Cloud Logging logs.
After writing analyses results to BigQuery, statistics data is exported to the mozanalysis bucket in GCS as JSON. The JSON data is accessed by the analysis dashboard to display results.
Architecture for Scaling Jetstream
To ensure analysis results are available in a timely manner, Jetstream implements two approaches for reducing the time required to run experiment analyses:
- Parallelization of experiment analyses using Argo
- Parallelization of lower-level calculations (statistics, segments, ...) using Dask
Parallelizing experiment analyses
Argo is a light-weight workflow engine for orchestrating parallel jobs on Kubernetes and is capable of creating tasks dynamically that will be executed in parallel. Using Argo, the analyses for different experiments and analysis dates are split into separate jobs that run in parallel on the jetstream Kubernetes cluster in the moz-fx-data-experiment-analysis GCP project.
Argo expects each step in the workflow to be a container. The existing Jetstream container, which has the Jetstream CLI installed, can be used for each of these steps.
The full workflow definition is defined in the workflows/run.yaml file.
Depending on how Jetstream is invoked (rerun, run-argo, or rerun_config_changed), Jetstream will determine the dates and experiments that are to be analyzed and injects them as parameters into run.yaml before launching the workflow. Argo will create separate jobs for each experiment and each analysis date. Once the analysis is complete, data gets exported as JSON to GCS.
Parallelizing lower-level calculations
In addition to running experiment analyses in parallel, Dask is used to parallelize lower-level calculations. The following steps could be executed in parallel:
- Analyses for each analysis period (daily, 28day, weekly, overall)
- Analyses for different segments
- Calculating statistics defined for an experiment analysis
The dask.delayed interface is used to turn the functions executing these steps into tasks that are added to a task graph which executes these steps in parallel. Dask is configured to use as many cores as are available on the machine by default, with 1 worker for each core. Multi-threading being avoided, instead processes are used since the code is dominated by Python code, otherwise there wouldn't be any speedup due Python's Global Interpreter Lock. To manually restrict the number of processes, the JETSTREAM_PROCESSES environment variable can be used.
Installation
Jetstream is executed on the jetstream Kubernetes cluster in the moz-fx-data-experiments project which is set up following Argo's installation guide:
- When creating or re-creating the cluster, BigQuery and Compute Engine read/write permissions need to be enabled
- Installing Argo:
- Create an
argonamespace:kubectl create ns argo - Install commonly used components:
kubectl apply -n argo -f https://github.com/argoproj/argo-workflows/releases/download/v3.4.5/install.yaml - Create new
clusterrole:kubectl create rolebinding default-admin --clusterrole=admin --serviceaccount=argo:default --namespace=argo
- Create an
- The
jetstreamDAG in Airflow triggers therun-argojob daily and either requires Compute Engine API access or the parameterscluster_ipandcluster_certneed to be provided- Currently the Airflow cluster does not have Compute Engine API access, so the cluster IP and certificate are stored as secrets and used for running Jetstream
Argo Workflow UI
Argo provides a Web UI to access running workflows. Users need to authenticate using a Bearer token:
- set
export CLOUDSDK_CORE_PROJECT=moz-fx-data-experiments - Get Bearer token and copy:
gcloud container clusters get-credentials jetstream --region=us-central1-a && kubectl -n argo exec $(kubectl get pod -n argo -l 'app=argo-server' --field-selector=status.phase=Running -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -- argo auth token - Connect to the Workflow UI using port forwarding:
kubectl -n argo port-forward svc/argo-server 2746:2746 - Open https://localhost:2746
- Use the generated Bearer token (including the word
Bearer) for authentication
Deleting Old Workflows
- The Workflow UI might get less responsive the more workflows have been run in the past
- To delete workflows that are older than 4 days run:
kubectl get wf -o go-template -n argo --template '{{range .items}}{{.metadata.name}} {{.metadata.creationTimestamp}}{{"\n"}}{{end}}' | awk '$2 <= "'$(gdate -d '30 days ago' -Ins --utc | sed 's/+0000/Z/')'" { print $1 }' | gxargs --no-run-if-empty kubectl delete wf -n argo
Cluster Updates
Argo updates should be tested on a separate cluster before applying them to production. Jetstream has some custom logic to connect to clusters and issue workflows that might be incompatible with future versions of Argo.
Preparation
- Ensure
kubectlis using the correct cluster context (e.g., to switch between dev and prod clusters)kubectl config get-contextskubectl config use-context <context>
- (optional) Check current Argo version
kubectl -n argo exec $(kubectl get pod -n argo -l 'app=argo-server' --field-selector=status.phase=Running -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -- argo version
- Check for breaking changes in the Argo Upgrade Guide
Perform Upgrade
- Find kubectl command to install/upgrade from the Argo releases page
- Should look like:
kubectl apply -n argo -f https://github.com/argoproj/argo-workflows/releases/download/v3.6.7/install.yaml- Change version number to most recent release
- Should look like:
- The GKE cluster itself is updated automatically by GCP
Post Upgrade
- Verify version number with command above and by checking UI
- Run a test workflow by sending a small analysis job to the cluster with
jetstream run-argofor a single experiment and date- Important Use configuration options to ensure production data is not overwritten
--bucket=None--dataset-id=<a test dataset>
- Use
--zoneand--cluster-idif using dev cluster
- Important Use configuration options to ensure production data is not overwritten
- Reset kubectl context if necessary
Tooling and Metric Versioning
Jetstream uses the same tooling and metric versions for an experiment across its entire analysis duration. This prevents inconsistent results, for example, when changes are made to how mozanalysis computes results or new default metrics are added in metric-hub mid-experiment.
Keeping track of tooling versions
When a new version of jetstream is released, for example after some library updates, a new Docker container gets pushed to the Artifact Registry. The container installs a specific version of each library and can be uniquely identified by a SHA256 hash. A timestamp indicating when the container was uploaded is also available.
Every time Jetstream runs and writes computed results to BigQuery, it tags the result tables with a last updated timestamp. However, the enrollments table won't update on new Jetstream runs, giving us an anchor from which to identify a consistent Jetstream image hash.
The last updated timestamp of the enrollments table is used to determine which Docker container was the most recently published one at that time. This container is then be used for all subsequent analyses.
The Artifact Registry API is used to access image information and to determine the container to use for the analysis based on the last updated timestamp of the experiments enrollment table.
Container hashes are passed to the Argo workflow config, which references docker containers used for execution.
Jetstream can be run using a specific image version using the --image_version parameter. The image can also be changed using the --image parameter.
Keeping track of metric-hub versions
Outcome and default configs can potentially change mid-experiment, leaving some experiments in an inconsistent state. Since these configs get pulled in dynamically and aren't installed as part of the Docker image the prior approach doesn't work here.
Instead, ConfigCollection.as_of(<date>) is used to checkout an earlier version of the repo as of the provided date.
This date will again be based on the last updated timestamp of the enrollments table. Calling as_of() will load the configs, defaults and outcomes that will subsequently be used for analysis. as_of() iterates through the commit history until it finds the first commit from before the last updated timestamp. If this commit is in a broken state (i.e., configs cannot be successfully loaded), as_of works forward from this point to find the closest working commit.
When making changes to experiment-specific configs, jetstream will automatically rerun the affected experiments which will result in the enrollments table getting updated and the most recent configs in metric-hub being used.
More information on how to use the most recent tooling and metric versions can be found here.